
WHAT IS FIXED PROSTHODONTICS?
Fixed prosthodontics is the branch of specialized area of dentistry, involved in the replacement of missing teeth with a cast prosthesis permanently cemented in place.

The fixed prosthesis can be in the form of single cast crown or multiple unit of cast crowns joined together, commonly referred to as fixed partial denture or bridge.


Objectives of fixed prosthesis
- To restore masticatory function
- To improve appearance
- To Improve speech
- To promote good oral hygiene
- To stabilize arch form and occlusion

Indications for fixed partial denture
- One or two adjacent teeth are missing in the same arch (short span edentulous area)
- When the supportive tissues are healthy.
- Suitable abutment teeth are present.
- The patient is in good health and desires to have the prosthesis placed.
- The patient has the skills and motivation to maintain good oral hygiene
- Patients preference
- Good oral hygiene

Contraindications for fixed partial denture
- Lack of supporting tissue and alveolar bone
- Presence of periodontal disease
- Excessive mobility of abutment teeth
- Patients with poor oral hygiene
- Patients who cannot afford treatment
Types of fixed Prostheses
1. Inlays

2. Onlays

3. Cast crowns:
a) Full coverage crown

b) Partial coverage crown
A restoration that restores all but one coronal surface of the crown is usually not restoring or covering the facial surface.
Types:
i) ¾ crowns
ii) Seven eight crown


4. Fixed partial denture or Bridges:
It is a type of cast restoration which replaces or restores one or more teeth that are cemented on the fixed or cemented onto the adjacent prepared tooth/ teeth.
FPD’s are usually referred in units i.e. 3-unit fpd which replaces one missing tooth and so on.


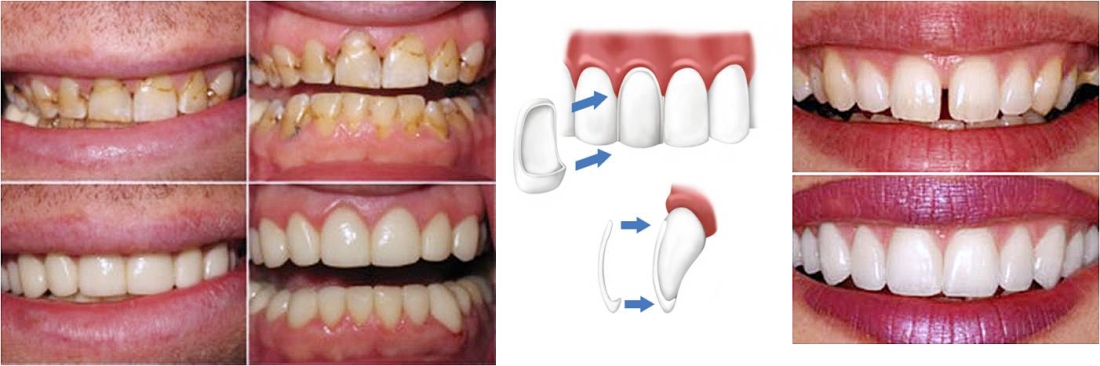
5. Veneers:
It is a layer of material placed over a tooth, either to improve the aesthetics of a tooth or to protect the tooth’s surface from damage.
a. Direct veneers are prepared directly on the patient’s tooth/teeth in the clinic. E.g.: direct composite veneers

b. Indirect veneers: are prepared in the laboratory and is cemented into the tooth. E.g.: porcelain laminate veneers
Crowns and Bridges
1. Classification of Crowns
Based on number of covered surfaces:
A) Full coverage (5 surfaces)
B) Partial coverage (Less than 5 surfaces)
A) Full Coverage Crowns
According to: A. Material B. Retention
B) Partial Coverage Crowns
According to: Retention
2. Classification of bridges
- Fixed – Fixed
- Fixed – Supported
- Fixed – Free (Cantilever)
- Spring Cantilever
- Removable
- Adhesive
1. Fixed-Fixed Bridge
It is a bridge in which the pontic is joined at both ends to the retainers by rigid connectors.

2. Fixed-Supported Bridge
It is a bridge in which the pontic is joined at one end to the retainer by a rigid connector, and the other end by a non rigid connector.
3. Fixed-Free Bridge (Cantilever)
It is a bridge in which the pontic is joined to the retainer at one end only, and the other end is free or unsupported.

4. Spring Cantilever Bridge
It is a bridge in which the pontic takes its support from a remote abutment by a resilient curved arm (palatal spring).

5. Removable Bridge
It is a bridge in which the connector is made up of two parts : one fixed to the retainer, and the other soldered to the pontic. The bridge can be removed by the patient for cleaning purposes.

6. Adhesive Bridge
It is a conservative bridge with minimum tooth preparation and retained on teeth by using a adhesive resin cement. Eg : Resin bonded bridges

Common Terminologies in Fixed Prosthodontics
- Tooth preparation: Is a clinical process where the natural tooth/teeth is prepared to receive a crown.

- Master cast and Die: Is the positive reproduction of the prepared tooth and consists of a suitable hard substance of sufficient accuracy (usually an improved stone, resin, or metal).

- Die pin or die system: Is a method of preparing the die on the master cast.

- Die spacer: A paint-on material that dries to a known thickness, used to provide space between a crown and the underlying tooth preparation.

- Wax pattern: A pattern of wax that, when invested and burned out or otherwise eliminated, will produce a mold in which a casting may be made.

- Dental Casting: Is the process by which a wax pattern of a restoration is converted to a replicate in dental alloy.
- Metal try-in

- Porcelain build-up or application

Materials used in fixed prosthesis
Dental casting alloys: are combination of two metal produced in specific proportion for fabrication of dental casting.
I. Classification by function:
a. Type I (soft): inlays
b. Type II (medium): inlays, onlays, crowns
c. Type III (hard): inlays, onlays, short span bridges
d. Type IV (extra hard): partial denture frameworks
Type III and type IV are generally termed as ‘crown and bridge alloys’.
II. Crown and bridge alloys:
This category of alloys include both noble and base metal alloys that are used in fabrication of full metal crowns and partial veneer crowns.
A) Noble metal alloys
- Gold based alloys: type III and type IV gold alloys
- Non-gold based alloys: silver-palladium alloys
B) Base metal alloys
- Nickle based alloys
- Cobalt based alloys
III. Metal-ceramic alloys:
A) Noble metal alloys for porcelain bonding
- Gold-platinum-palladium alloy
- Gold-palladium-silver alloy
- Gold-palladium alloy
- Palladium-silver alloy
- High-palladium alloy
B) Base metal alloys for porcelain bonding
- Nickle-chromium alloy
- Cobalt-chromium alloy
C) Removable partial denture alloys
- Nickle-chromium alloy
- Cobalt-chromium alloy
- Cobalt-chromium-nickle alloy
Dental Investment material
They are the mold materials used in the casting of dental gold alloys with liquidus temperatures no more than 1080 ºc.

Classification:
A. Gypsum bonded investment
B. Phosphate bonded investment
C. Silica bonded investment

- A tooth serving as an attachment for a fixed partial denture is called an abutment.
- The artificial tooth suspended from the abutment teeth is a pontic.
- The pontic is connected to the fixed partial denture retainers, which are extracoronal restorations that are cemented to the prepared abutment teeth.
- The connectors between the pontic and the retainer may be rigid (ie, solder joints or cast connectors) or non-rigid (ie, precision attachments or stress breakers).
Steps in the Fabrication of a Fixed Partial Denture

– end –
I didn’t realize that there were so many different kinds of crowns and bridges! My dad is getting to an age where his dental health is depreciating quickly. He may eventually need a bridge by the end of the year, so I’ll have to make sure to find him a good prosthodontist nearby.
LikeLike